The NCERT Solution For Class 10 Geography Chapter 6 – “Manufacturing Industries” provides detailed answers to all the questions in the chapter. This chapter discusses the importance of the manufacturing sector in India’s economic development and its contribution to employment, income generation, and export earnings. It covers various types of industries, such as agro-based, mineral-based, chemical, engineering, and textile industries, and examines their distribution, environmental concerns, and the need for sustainable development.
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Geography Chapter 6 – Manufacturing Industries

Here Are The NCERT Solution For Class 10 Geography Chapter 6
Exercises
- Multiple choice questions.
(i) Which one of the following industries uses limestone as a raw material.
a) Aluminium
(b) Cement
(c ) Sugar
(d) Jute
Solution: (b) Cement
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Geography Chapter 6
(ii) Which one of the following agencies markets steel for the public sector plants?
a) HAIL
(b) SAIL
(c ) TATA Steel
(d) MNCC
Solution: (b) SAIL
(iii) Which one of the following industries uses bauxite as a raw material?
a) Aluminium
(b) Cement
(c ) Jute
(d) Steel
Solution: (a) Aluminium
(iv) Which one of the following industries manufactures telephones, computer, etc?
a) Steel
(b) Electronic
(c ) Aluminium
(d) Information Technology
Solution: (b) Electronic
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Geography Chapter 6
- Answer the following briefly in not more than 30 words.
(i) What is manufacturing?
Solution:
Large-scale production of goods following the processing of raw materials to create more valuable products is known as manufacturing. Wood is used to make paper, sugar is made from sugarcane, iron ore is used to make steel, and bauxite is used to make aluminium.
(ii) Name any three physical factors for the location of the industry.
Solution: There are three physical factors that determine where an industry is located:
- The availability of raw materials
2. Near the market
3. The availability of electricity
For instance, the Hugli basin contains jute-producing regions, and jute can be processed and transported by inexpensive waterways, which is why the jute textile industry is concentrated in West Bengal.
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Geography Chapter 6
(iii) Name any three human factors for the location of an industry.
Solution: There are three human factors that determine where an industry should be located:
1. Workforce
2. Funds
3. Nearness to urban areas
For instance, West Bengal’s jute textile industry benefits from cheap labour from the states that border it, and Kolkata serves as a major urban hub for port, banking, and insurance services.
(iv) What are the basic industries? Give an example.
Solution: The sectors that provide their product or the raw materials needed to make other goods are known as basic or key industries.
For instance, other industries use iron and steel as raw materials from the iron and steel industries.
(v) Name the important raw materials used in the manufacturing of cement.
Solution: The following are significant raw materials that go into making cement:
1.Limestone
2. Silica
3. Luminous
4. gypsum
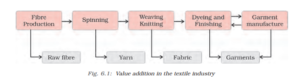
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Geography Chapter 6
- Write the answers to the following questions in 120 words.
(i) How are integrated steel plants different from mini steel plants? What problems does the industry face? What recent developments have led to a rise in the production capacity?
Solution: Large integrated steel plants manage all processes in-house, from raw material assembly to steel production, rolling, and shaping.
Smaller in size, using sponge iron and steel scrap, mini steel plants are equipped with electric furnaces. Additionally, they have rerollers that work with steel ingots. They manufacture mild and alloy steel that meets specified requirements.
The following lists the difficulties the steel sector is facing:
1. The expensive and scarce supply of coking coal
2. Reduced labour productivity 3. An irregular energy supply
4. Substandard facilities
The industry has benefited from recent developments like liberalisation and foreign direct investment (FDI) thanks to the efforts of private business owners.
(ii) How do industries pollute the environment?
Solution: There are four categories of pollution that industries cause:
1. The air
2. H2O
3. Terrain
- Sounds
When there is a significant concentration of unwanted gases, such as carbon monoxide, sulphur dioxide, and airborne particulate matter, air pollution results.
Both organic and inorganic industrial wastes and effluents that are dumped into water bodies are the source of pollution in water bodies. The principal offenders are paper, refineries, and tanneries.
Pollution of soil and water is closely related. The soil becomes unusable for farming when waste is dumped on it. The contaminants then infiltrate the groundwater by way of the soil.
Industrial machinery and construction activities are the primary sources of noise pollution.
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Geography Chapter 6
(iii) Discuss the steps to be taken to minimise environmental degradation by industry.
Solution:
The actions that can be taken to reduce industrial environmental degradation are listed below:
1. Increasing energy efficiency by implementing the newest methods and modernising current equipment.
2. Establishing green spaces to preserve ecological harmony.3. Installing smokestacks in factories equipped with fabric filters, scrubbers, electrostatic precipitators, and inertial separators can help lower the amount of particulates in the air.
4. Silencer use for equipment that produces noise.
5. Reducing water use by recycling and reusing it in two or more phases.
6. Rainwater collection to fulfil water needs
7. Handling wastewater and hot water before dumping them into ponds and rivers. There are three stages to the treatment of industrial effluents:
Initial mechanical treatment
(a). This process includes sedimentation, flocculation, grinding, and screening.
b. Biological processes for secondary treatment
c. Triennial processing through chemical, physical, and biological methods. Wastewater is recycled in this process.
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Geography Chapter 6
For the Next Chapter Solution Click Below
CHAPTER 1 – Resources and Development
CHAPTER 2 – Forest and Wildlife Resources
CHAPTER 5 – Minerals and Energy Resources
CHAPTER 6 – Manufacturing Industries
CHAPTER 7 – Lifelines of the National Economy

