NCERT Solution For Class 10 Economics Chapter 2 – Sectors of the Indian Economy

NCERT Solution For Class 10 Economics Chapter 2
- Fill in the blanks using the correct option given in the bracket:
- Employment in the service sector _________ increased to the same extent as production. (has / has not)
- Workers in the _________ sector do not produce goods. (tertiary / agricultural)
- Most of the workers in the _________ sector enjoy job security. (organised / unorganised)
- A _________ proportion of labourers in India are working in the unorganised sector. (large / small)
- Cotton is a _________ product and cloth is a _________ product. [natural /manufactured]
- The activities in primary, secondary and tertiary sectors are_________ [independent / interdependent]
Answer a: has not
Answer b: tertiary
Answer c: organised
Answer d: large
Answer e: natural and manufactured
Answer f: interdependent
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Economics Chapter 2
2. Choose the most appropriate answer.
a. The sectors are classified into public and private sector on the basis of:
- employment conditions
- the nature of economic activity
- ownership of enterprises
- number of workers employed in the enterprise
Answer: 3. ownership of enterprises
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Economics Chapter 2
b. Production of a commodity, mostly through the natural process, is an activity in _________ sector.
- primary
- secondary
- tertiary
- information technology
Answer: 1. primary
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Economics Chapter 2
c. GDP is the total value of _________ produced during a particular year.
- all goods and services
- all final goods and services
- all intermediate goods and services
- all intermediate and final goods and services
Answer: 2. all final goods and services
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Economics Chapter 2
d. In terms of GDP the share of tertiary sector in 2013-14 is between _________ per cent.
- 20 to 30
- 30 to 40
- 50 to 60
- 60 to 70
Answer: 3. 50 to 60
3. Match the following:
| Problems faced by farming sector | Some possible measures |
| 1. Unirrigated land | (a) Setting up agro-based mills |
| 2. Low prices for crops | (b) Cooperative marketing societies |
| 3. Debt burden | (c) Procurement of food grains by government |
| 4. No job in the off season | (d) Construction of canals by the government |
| 5. Compelled to sell their grains to the local traders soon after harvest | (e) Banks to provide credit with low interest |
Answer:
| Problems faced by farming sector | Some possible measures |
| 1. Unirrigated land | (d) Construction of canals by the government |
| 2. Low prices for crops | (c) Procurement of food grains by government |
| 3. Debt burden | (e) Banks to provide credit with low interest |
| 4. No job in the off season | (a) Setting up agro-based mills |
| 5. Compelled to sell their grains to the local traders soon after harvest | (b) Cooperative marketing societies |
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Economics Chapter 2
- Find the odd one out and say why.
(i) Tourist guide, dhobi, tailor, potter
Answer:While potters, tailors, and dhobi own their private businesses, tourist guides are the exception, appointed by a government department.
(ii) Teacher, doctor, vegetable vendor, lawyer
Answer: Being employed in the primary sector, whereas teachers, lawyers, and doctors are employed in the tertiary sector, makes the vegetable vendor stand out.
(iii) Postman, cobbler, soldier, police constable
Answer:Cobbler stands out from the others as he is employed by the private sector, whereas the postman, soldier, and police constable are employed by the public or organised sector.
(iv) MTNL, Indian Railways, Air India, Jet Airways, All India Radio
Answer: The exception is Jet Airways, which is privately held while MTNL, Indian Railways, Air India, and All India Radio are owned by the Indian government.
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Economics Chapter 2
5. A research scholar looked at the working people in the city of Surat and found the following.
| Place of Work | Nature of Employment | Percentage of working People |
| In offices and factories registered with the government | Organised | 15 |
| Own shops, office, clinics in marketplaces with formal license |
15 | |
| People working on the street, construction workers, domestic workers |
20 | |
| Working in small workshops usually not registered with the government |
Complete the table. What is the percentage of workers in the unorganised sector in this city?
Answer:
| Place of Work | Nature of Employment | Percentage of working People |
| In offices and factories registered with the government | Organised | 15 |
| Own shops, office, clinics in marketplaces with formal license | Organised | 15 |
| People working on the street, construction workers, domestic workers | Unorganised | 20 |
| Working in small workshops usually not registered with the government | Unorganised | 50 |
The percentage of workers in the unorganised sector are 70% (50+20)
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Economics Chapter 2
6. Do you think the classification of economic activities into primary, secondary and tertiary is useful? Explain how.
Answer: The primary, secondary, and tertiary economic activity classifications are helpful in categorising the various jobs that people in the nation hold and the relative contributions of each sector to the nation’s economic development. It is also crucial because it makes clear which industries contribute the most to GDP and which have the potential to grow employment and national income.
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Economics Chapter 2
- For each of the sectors that we came across in this chapter why should one focus on employment and GDP? Could there be other issues which should be examined? Discuss.
Answer:Two of the most crucial elements in a nation’s development are its GDP and employment rate. A nation’s total productivity and national income are determined by its employment and GDP. GDP, national income, and per capita income all naturally rise in a nation with a high employment rate. For this reason, this chapter has focused primarily on these two points. The following are additional matters that need to be looked into:
1. Medical establishments
2. Instruction3. Indigence
4. Manufacturing of Food
5. Food - Make a long list of all kinds of work that you find adults around you doing for a living. In what way can you classify them? Explain your choice.
Answer:The three categories of human endeavours that comprise their livelihood are primary, secondary, and tertiary. Observing those around us, we are able to categorise their employment sector into one of the three groups. The primary sector includes things like cleaning, farming, and vegetable sales. One example of the secondary sector is the manufacturing of goods. Among the industries in the tertiary sector are banking, mining, teaching, and transportation.
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Economics Chapter 2
9. How is the tertiary sector different from other sectors? Illustrate with a few examples.
Answer: Tertiary activities are those that support the growth of the primary and secondary sectors of the economy. The primary and secondary sector activities are not the same as these. These actions assist or support the production process rather than producing a good on their own. Products made in the primary or secondary sector, for instance, would need to be shipped by trucks or railroads before being offered for sale in wholesale and retail establishments. The tertiary sector includes these retail establishments and transportation facilities. They don’t make anything, but they are crucial in getting those goods on the market and selling them.
10.What do you understand by disguised unemployment? Explain with an example each from the urban and rural areas.
Answer:Disguised unemployment is the state of underemployment in which individuals appear to be working but are all forced to work less than their potential. In this instance, the individual thinks of himself as employed, but in reality, he is not. This type of unemployment is common in rural areas where agriculture serves as the primary source of income.
Two additional workers are considered to be experiencing disguised unemployment if a piece of land only needs three people to work on it, but five people are working on it instead. When professionals like painters, plumbers, and electricians struggle to find work on a daily basis and put in far less time at work than they could, it’s known as disguised unemployment in urban areas.
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Economics Chapter 2
11. Distinguish between open unemployment and disguised unemployment.
Answer: A person who is educated and willing to work but is unable to find employment is said to be unemployed. This type of unemployment is apparent. However, when someone appears to be employed but is forced to work less than their potential, that situation is known as disguised unemployment. This type of employment is clearly visible in villages where farm workers think they are employed even though they are not working as much as they could be.
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Economics Chapter 2
12.“Tertiary sector is not playing any significant role in the development of Indian economy.” Do you agree? Give reasons in support of your answer.
Answer: This is not accurate, no. The growth of the Indian economy is greatly aided by the tertiary sector. The primary sector was supplanted as the nation’s most productive sector by the tertiary sector in 2003. Here are some justifications for this:
1. The tertiary sector is necessary to sustain the growth of the primary and secondary sectors.
2. The tertiary sector significantly increases the nation’s national income.
3. Under the tertiary sector is education, which is the foundation of everything. A teacher is considered to be employed in the tertiary sector.
4. This industry offers the nation’s workforce the greatest number of job opportunities.
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Economics Chapter 2
- Service sector in India employs two different kinds of people. Who are these?
Answer:In India, there are two types of workers in the service sector. They include: 1. Highly Skilled Labour, such as bankers, teachers, IT officials, and so on. These individuals work there on a permanent basis.
2. Less Skilled Labour: This category comprises contractors, electricians, plumbers, and so on. It is not a permanent job for these people.
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Economics Chapter 2
14. Workers are exploited in the unorganised sector. Do you agree with this view? Give reasons in support of your answer.
Answer: Small, dispersed organisations that operate primarily outside of government authority define the unorganised sector. Although rules and regulations exist, they are not adhered to. There are irregular and poorly paid jobs here. Therefore, it is accurate to state that employees in the unorganised sector are exploited because they are required to perform more work than they are paid for. There are no provisions for overtime compensation or health benefits. The lack of job security is the main issue for those who work in this industry.
15. How are the activities in the economy classified on the basis of employment conditions?
Answer: Two sectors can be distinguished in the economy based on the employment situation:
1. The Organised Sector: Businesses that are officially recognised by the Indian government and that offer competitive pay and a welcoming work environment to their staff.
The unorganised sector consists of transient, small, dispersed units. This industry pays its workers less.
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Economics Chapter 2
16. Compare the employment conditions prevailing in the organised and unorganised sectors.
Answer: Employees in the organised sector receive permanent employment, better pay, health benefits, and a clean workplace. They won’t necessarily search for a new job every day. In the unorganised sector, workers are exploited, wages are low, no overtime pay is offered, no medical benefits are offered, and the working conditions are hazardous.
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Economics Chapter 2
17. Explain the objective of implementing the NREGA 2005.
Answer:The National Rural Employment Guarantee Act of 2005 was enacted with the intention of guaranteeing 100 days of employment annually to all individuals who require employment. Additionally, it stipulates that jobless people will receive employment wages in the event that this act does not result in employment. People living in villages and smaller towns need more work opportunities to be created.
18. Using examples from your area, compare and contrast the activities and functions of private and public sectors.
Answer:While businesses and industries are owned by the government in the public sector, private sector assets are owned by private individuals. While the public sector works to earn profits and provide facilities for the general public, the private sector works to make profits. Government banks, post offices, local hospitals, and Indian railways are a few typical instances of the public sector that we encounter every day. The private sector is commonly represented by establishments like IT firms, shopping centres, and multiplexes, among others.
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Economics Chapter 2
19. Discuss and fill the following table giving one example each from your area.
| Well-Managed Organisation | Badly-Managed Organisation | |
| Public Sector | ||
| Private Sector |
Answer: Students must answer this question based on their own observations.
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Economics Chapter 2
20. Give a few examples of public sector activities and explain why the government has taken them up.
Answer: The goals of public sector initiatives are to benefit the general public. The public sector was taken over by the government in order to give the nation’s citizens access to adequate facilities. The public sector includes banks, transportation, irrigation, electricity, water, and all other necessities for human habitation. The government is in charge of giving its citizens access to these facilities.
- Explain how the public sector contributes to the economic development of a nation.
Answer:The sector that reports to the Indian government is called the public sector. The basic needs of people, such as water, electricity, and irrigation, all fall under this category, which is why the government has assumed responsibility for it. The failure of a nation’s economy stems from the fact that unchecked growth in these departments will cease national development. A nation’s economic progress is reliant on the welfare of its populace; in the event that this latter is compromised, the nation’s economic progress will also be impacted. Under this section, the government creates jobs and supports the growth of both large and small businesses. - The workers in the unorganised sector need protection on the following issues : wages, safety and health. Explain with examples.
Answer: Small, dispersed organisations that operate primarily outside of government authority define the unorganised sector. Although rules and regulations exist, they are not adhered to. Employees in the unorganised sector require safeguards:
Pay: Workers in the unorganised sector earn an income that is not fixed and barely covers their basic needs. Therefore, in order for these workers to develop and support the growth of the nation, they should be paid fair and fixed wages. A painter, for instance, would only be paid for the days he works; on the other days, he would be unemployed and unable to make any money.
Workers in the unorganised sector are not given any safety measures. There is no job security, and employees may be fired or removed from their position at any time in accordance with worker demands. For instance, once building construction is finished, a labourer working on the project is out of a job and cannot be guaranteed one again.
Health: The nation’s growth and development are greatly influenced by its state of health. There is no medical security provided to the unorganised sector, and employers are not held accountable for employees’ health in the event of an accident that occurs on the job. Workers paid on a daily basis, for instance, are not eligible for sick leave.
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Economics Chapter 2
- A study in Ahmedabad found that out of 15,00,000 workers in the city, 11,00,000 worked in the unorganised sector. The total income of the city in this year (1997-1998) was Rs 60,000 million. Out of this Rs 32,000 million was generated in the organised sector. Present this data as a table. What kind of ways should be thought of for generating more employment in the city?
Answer:
| Total Workers | Workers in Unorganised Sector | Total Income of City (1997-1998) | Income generated by organised sector | Income generated by unorganised sector |
| 15,00,000 | 11,00,000 | 60,000 million | 32,000 million | 28,000 million |
The table unambiguously demonstrates that the revenue produced in Ahmedabad’s unorganised sector accounts for nearly half of the city’s total revenue. To boost job prospects for the populace, more industries ought to be established, everyone should have access to quality education, and everyone should have access to quality facilities in the public sector.
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Economics Chapter 2
- The following table gives the GDP in Rupees (Crores) by the three sectors:
| Year | Primary | Secondary | Tertiary |
| 2000 | 52,000 | 48,500 | 1,33,500 |
| 2013 | 8,00,500 | 10,74,000 | 38,68,000 |
(i) Calculate the share of the three sectors in GDP for 2000 and 2013
(ii) Show the data as a bar diagram similar to Graph 2 in the chapter.
(iii) What conclusions can we draw from the bar graph?
Answer:
(i) In 2000, primary sector = 22.22%, secondary sector = 20.73%, tertiary sector = 57.04% And In 2013, primary sector = 13.94%, secondary sector = 18.70%, tertiary sector = 67.36% (ii)
ii)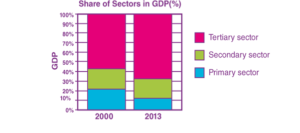
(iii) We can draw the conclusion that the share of the tertiary sector in the GDP has increased by 10%, while that of the primary sector has almost halved. The secondary sector has grown by about 2% in the last 13 years.
NCERT Solution For Class 10 Economics Chapter 2
For the Next Chapter Solution Click Below
CHAPTER 2 – Sectors of the Indian Economy
CHAPTER 4 – Globalisation and the Indian Economy
For more updates, you can follow us on our social media