NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 -Control And Coordination
Best NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Control And Coordination .We will examine the complex processes in this chapter that allow organisms to respond to their surroundings and preserve homeostasis. The processes of coordination and control are crucial for ensuring adaptation, growth, and survival.
Intext Exercise 1
1. What is the Difference Between a Reflex Action and Walking?
Answer: Walking differs from a reflex response in the following ways:
|
Reflex Action |
Walking |
|
A reflex action is a quick, involuntary response to an external stimulus. |
Walking is an action that one engages in willingly. |
|
It does not require any thought. |
While walking, we have conscious control over it. |
|
Walking offers activities that do not require an organism’s or an organ’s survival and protection. |
The purpose of reflex response is to help organs or organisms survive and be protected. |
2. What Happens at the Synapse Between Two Neurons?
Answer:
1.Neurones, which include acetylcholine, are released when a nerve impulse reaches the end of an axon.
2. At the axon-dendrite junction, neurotransmitters travel between the axon and dendrites of the subsequent neurone. This point is known as a synapse.
3. Neurotransmitters attach themselves to the membranes of the dendrites, enabling the nerve impulse to enter the receiving neurone and travel to the intended location. (Cells in muscles)
3. Which Part of the Brain Maintains Posture and Equilibrium of the Body?
Answer: One part of the hindbrain that controls posture and balance in the body is the cerebellum.
4. How Do We Detect the Smell of an Agarbatti (Incense Stick)?
Answer:
Olfactory receptors in our noses pick up on the aroma of an incense stick when it gets there. The forebrain interprets it by merging it with data from other receptors and data that has already been mentally stored as memory.
5. What is the Role of the Brain in Reflex Action?
Answer: Reflex action is the term for humans’ quick, involuntary reaction to stimuli, or abrupt changes in their surroundings. The motor nerves, which regulate muscle action, are connected to the sensory nerves, which pick up on stimuli.
The link between an effector’s instantaneous response (output) and a signal received from receptors (input) is known as a reflex arc. The reflex arc serves as the pathway for communication between effectors and receptors during a reflex action.
Signalling is carried out by sensory and motor neurones that are connected to one another in the spinal cord. Reflex arcs begin in the spinal cord, but the brain receives the information (input). The brain is only aware of the signal and the response that have taken place. The memory of the brain contains this information.
This facilitates the training of particular reflexes. Conversely, the brain plays no role in the response’s creation.
Best NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Control And Coordination
1. What are Plant Hormones?
Answer: Plant hormones, sometimes referred to as phytohormones, are organic substances that are found in nature and control the growth and metabolism of plant cells. The plant produces them in one area of its body, then moves them to other areas as required. There are five main categories of plant hormones: ethylene, gibberellins, cytokinin, abscisic acid, and auxins.
2. How is the Movement of Leaves of the Sensitive Plant Different From the Movement of a Shoot Towards Light?
Answer: The delicate Mimosa pudica plant, popularly referred to as “touch me not,” responds to touch or contact stimuli by moving its leaves. This is some kind of nastic movement. Disparities in the turgor pressures of leaf cells generate this kind of phenomenon. Growth has no relevance to this motion. These motions are not symmetrical.
A shoot migrating towards the direction of light is called phototropism. One-directional growth is the cause of these trophic shifts. This means that this type of movement is directed and growth-dependent. One instance of phototropism is the movement of a sunflower towards the sun.
3. Give an Example of a Plant Hormone That Promotes Growth.
Answer: One plant hormone that encourages growth is auxin.
4. How Do Auxins Promote the Growth of a Tendril Around a Support?
Answer:
At the tip of the plant’s shoot is where auxin, the growth hormone, is created. At the tips of the shoots, it encourages the formation of longer cells. When auxin comes into contact with a support, it causes the cells on the other side of the tendril to develop more quickly, leading to uneven growth on both sides of the tendril.
The tendril wraps around the support as a result. Because of this, as the tendrils loop around the support, they have the appearance of a watch spring.
5. Design an Experiment To Demonstrate Hydrotropism.
Answer: Hydrotropism is the movement of plant parts in response to water. Roots show positive hydrotropism when they grow in the direction of water. For instance: Put the letters A and B on two little beakers. Pour some water into Beaker A.
Roll out the filter paper to create a bridge between Beaker A and Beaker B, as shown in the diagram below. Plant a couple of the growing seeds in the middle of the filter paper bridge. To prevent the moisture from escaping, place a clear plastic container over the entire setup.
Best NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Control And Coordination
Intext Exercise 3
1. How Does Chemical Coordination Take Place in Animals?
Answer: Animals use hormones to help regulate their chemical responses. Hormones are chemical messengers that regulate several physiological functions of organisms. The body’s glands generate it. Organs that are frequently distant from the gland are affected by hormones. Consequently, these hormones are transported to the organ of action via glands in the circulation.
The endocrine system is in charge of hormone coordination and control, as well as the regulation of physiological processes. Our bodies’ physiological processes are regulated and coordinated by the nervous system and endocrine system.
2. Why is the Use of Iodised Salt Advisable?
Answer: The body uses iodine from food to help produce thyroxine.
A low thyroid hormone causes the thyroid gland to swell. This may lead to a straightforward case of goitre.
Best NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Control And Coordination
3. How Does Our Body Respond When Adrenaline Is Secreted Into the Blood?
Answer: The alternate names for adrenaline and noradrenaline are epinephrine and norepinephrine, respectively. The hormone adrenaline stimulates the sympathetic nervous system. It gets the body ready for everything that could come up. Adrenaline secretion is the cause of fear, perspiration, shivering, and other bodily reactions.
All of these reactions increase the amount of oxygen that reaches the muscles while breathing, which frees up more energy for movement or combat. Consequently, adrenaline equips the body to handle any stress or calamity. It is hence sometimes referred to as the “emergency hormone.”
4. Why are Some Patients of Diabetes Treated by Giving Injections of Insulin?
Answer: In diabetes mellitus, the blood sugar (glucose) level is excessively elevated. The pancreas secretes the hormone insulin, which helps the liver convert excess glucose to glycogen, which helps control blood sugar levels.
For these individuals, the pancreas does not release enough insulin to convert glucose to glycogen. Insulin injections are used to treat diabetic individuals because of this.
NCERT Exercises
1. Which of the Following is a Plant Hormone?
-
Insulin (b) Thyroxin (c) Oestrogen (d)Cytokinin
Answer: Cytokinin
2. Question 2: The Gap Between Two Neurons is Called a
(a) dendrite. (b) synapse. (c) axon. (d) impulse.
Answer: Synapse
3. The Brain is Responsible For
(a) thinking. (b) regulating the heartbeat.
(c) balancing the body. (d) all of the above.
Answer: All of the above
4. What is the Function of Receptors in Our Body? Think of Situations Where Receptors Do Not Work Properly. What Problems are Likely To Arise?
Answer: Receptor cells are sensory cells. They are typically present in our sense organs, which include the nose, tongue, eyes, skin, and inner ear. The following are the roles of receptors:
-They are sensitive to cues from their surroundings, such as discomfort or heat.
-Additionally, they send a message to the spinal cord by inducing a sensory neuron’s impulse. When receptors are destroyed, the brain is unable to perceive external impulses that convey messages. The tissues and organs of the body could be harmed by this. For instance, someone may not be able to hear when someone calls them out if their receptors are broken.
Best NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Control And Coordination
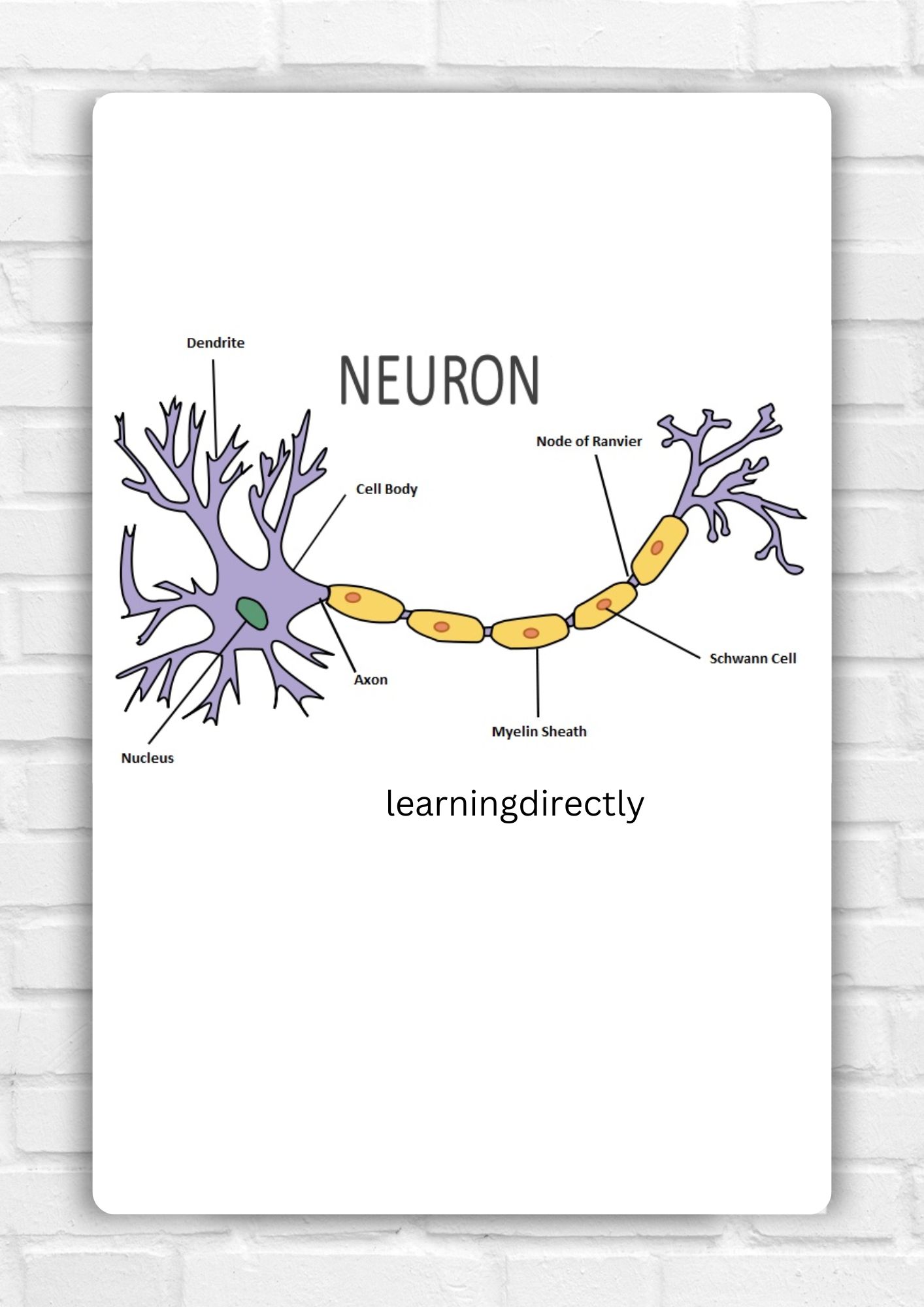
5. Draw the Structure of a Neuron and Explain Its Function.
Answer: The structural and functional unit of the nervous system is known as a neurone. A neuron’s three main parts are the axon, dendrite, and cell body.
A Neuron’s Functions Include:
1. The movement of impulses into the brain or spinal cord from the outside world.
2. Coordination of the brain and spinal cord with other organs.
6. How Does Phototropism Occur in Plants?
Answer: Phototropism is the term for the movement of plant components in response to light. In contrast to roots, which are phototropic in a negative sense, shoots exhibit positive phototropism. Plant phototropism is caused by auxins such as indole-acetic acid (IAA). If one side of the shoot is exposed to sunlight, the IAA molecules move to the other, shaded side.
IAA causes cell division and elongation on the shaded side of the shoot rather than the light-exposed side. This results in unequal growth on both sides of the stalk, with the shaded side growing faster than the sunny side. As a result, the shoot bends toward the light.
7. Which Signals Will Get Disrupted in Case of a Spinal Cord Injury?
Answer: If the spinal cord is damaged, all nerve signals will be interfered with. This will affect how impulses go from receptors to the brain and how the brain responds to effectors, especially motor neurones.
Best NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Control And Coordination
8. How Does Chemical Coordination Occur in Plants?
Answer: Plants respond to stimuli by moving their leaves. A specific class of chemical molecules known as plant hormones or phytohormones regulates and coordinates plant growth, development, and reaction to the environment. Plant hormones are made in a specific area of the plant and are relocated to other sections of the body.
When a hormone produced in roots is needed, it is translocated to other sections of the plant. Auxins, gibberellins, cytokinin, abscisic acid, and ethylene are the five major types of phytohormones. Auxins, gibberellins, cytokinin, and ethylene are examples of growth promoters, while abscisic acid is an example of growth inhibitor.
9. What is the Need for a System of Control and Coordination in an Organism?
Answer: The process of keeping the body functioning in response to changes in the body by cooperating for various integrated bodily systems is known as coordination. Every movement brought on by a stimulus needs to be painstakingly timed and regulated. Developing more effective response mechanisms is facilitated by being able to regulate your response to stimuli.
The organism’s capacity to operate effectively depends on the coordination of multiple reactions when all stimuli and their effects are considered. Consequently, a synchronisation of different physiological processes and responses is required. Animals can control and coordinate their movements thanks to their neurological and muscular systems. Phytohormones are in charge of directing and coordinating the behaviour of plants.
10. How are Involuntary Actions and Reflex Actions Different From Each Other?
Answer: Involuntary actions are beyond our ability to control. We can’t control the movement of food in the alimentary canal, for example. These actions, on the other hand, are directly controlled by the brain. On the other hand, reflex behaviours such as pulling back the hand when it comes into contact with a hot object are instantaneous and do not require any thought.
This suggests that reflex actions are not brain-controlled, in contrast to involuntary actions. Reflex actions can be conditioned, while involuntary actions like heartbeat and peristalsis cannot. Though not all involuntary actions are reflex actions, it is possible to draw the conclusion that they are all reflex actions.
Best NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Control And Coordination
For the Next Poem Solution Click Below
CHAPTER 1 – Chemical Reactions and Equations
CHAPTER 2 – Acid, Bases and Salts
CHAPTER 3 – Metals and Non-metals
CHAPTER 4 – Carbon And Its Compounds
CHAPTER 6 – Control And Coordination
CHAPTER 7 – How do Organisms Reproduce
CHAPTER 8 – Heredity and Evolution
CHAPTER 9 – Light Reflection and Refraction
CHAPTER 10 – The Human Eye and the Colourful World
CHAPTER 12 – Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
For more updates, you can follow us on our social media