NCERT Solutions for Science Class 10chapter 4-carbon and its compound
Best NCERT Solutions for Chapter 4 Science Class 10 Carbon And Its Compounds .The element carbon is amazing; it is the building block of all biological life. Carbon is able to form a remarkable diversity of compounds due to its exceptional ability to form bonds with a wide range of other elements. Its ability to establish four covalent bonds with other atoms, or tetravalency, is largely responsible for its versatility.
Best NCERT Solutions for Chapter 4 Science Class 10 Carbon And Its Compounds
Intext Exercise 1
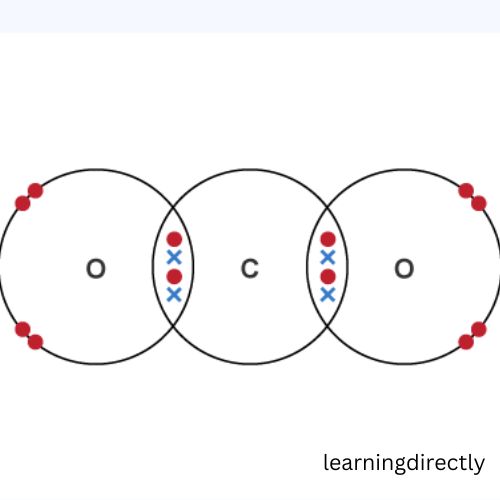
1: What would be the electron dot structure of carbon dioxide which has the formula CO2?
Answer: The CO2 cross-dot structure is-
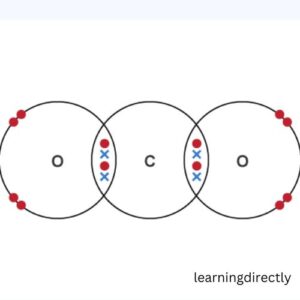
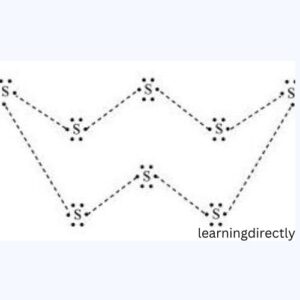
2: What would be the electron dot structure of a molecule of sulphur which is made up of eight atoms of sulphur? (Hint – The eight atoms of sulphur are joined together in the form of a ring.)
Answer: A S8 molecule’s dot structure:
Best NCERT Solutions for Chapter 4 Science Class 10 Carbon And Its Compounds
Intext Exercise 2
1: How many structural isomers possible for pentane?
Answer:
Pentane has three structural isomers.
(i) CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3.
(ii)CH3CH(CH3)CH2CH3
(iii) C(CH3)4
2: What are the two properties of carbon to form a large number of compounds?
Answer: Carbon has two characteristics that allow it to generate a wide variety of compounds:
(i) Catenation: The capacity to unite with oneself. It is the capacity for self-linking.
(ii) Tetravalency: Only four bonds can be formed by carbon. Tertravalency is the term used to describe that atomic arrangement.
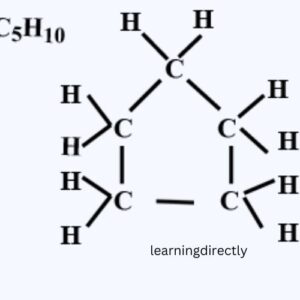
3: What will be the formula and electron dot structure of cyclopentane?
Answer: C5H10 is the formula for cyclopentane.
4: Draw the structures for the following compounds.
(i) Ethanoic acid
(ii) Bromopentane
(iii) Hexanal
(iv) Butanone
Answer: (i) Ethanoic acid
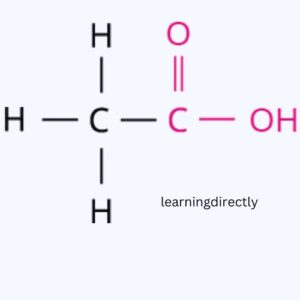
(ii) CH3CH2CH2CH(Br)CH3
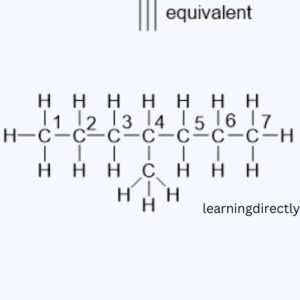
(iii) Hexanal
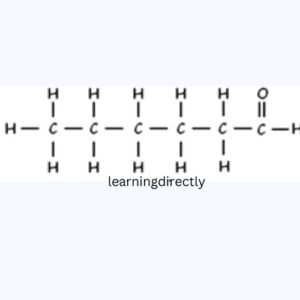
(iv) Butanone
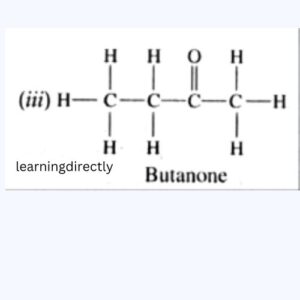
5: Write the name of the following compounds.
(i)
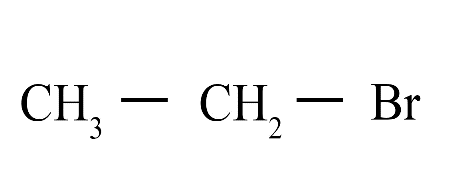
(ii)
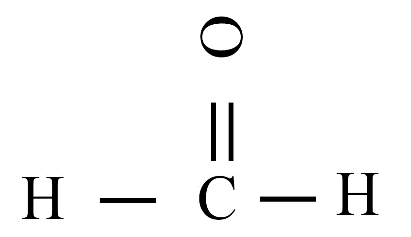
(iii)
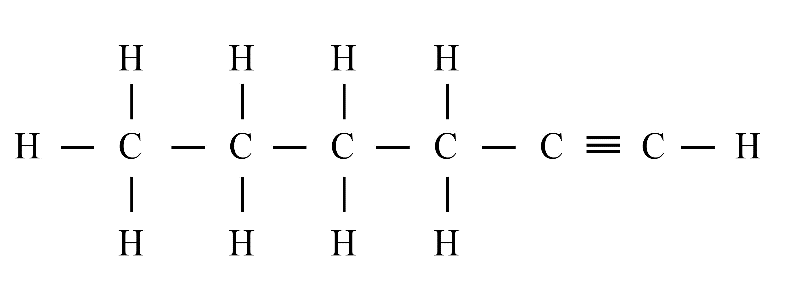
Answer:
(i) Bromoethane
(ii) Methanal
(iii) Hexyne
Best NCERT Solutions for Chapter 4 Science Class 10 Carbon And Its Compounds
Intext Exercise 3
1: Why is the conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid an oxidation reaction?
Answer: the process by which oxygen is added to ethanol to transform it into ethanoic acid. It is a reaction of oxidation.
C2H5OH −→−[O]
CH3COOH
2: A mixture of oxygen and ethyne is burnt for welding. Can you tell why a mixture of ethyne and air is not used?
Answer: When ethyne is burnt in the air, it gives a sooty flame due to its unsaturation nature. if ethyne is burnt with oxygen, it gives a clear flame at a temperature of 2500°C because of complete combustion. Oxy-acetylene flame is used for welding. It is difficult to attain this much high temperature without mixing oxygen that’s why a mixture of ethyne and air is not used.
Best NCERT Solutions for Chapter 4 Science Class 10 Carbon And Its Compounds
Intext Exercise 4
1: Distinguish experimentally between an alcohol and carboxylic acid.
Answer: Only carboxylic acid reacts with carbonates and bicarbonates when alcohol and carboxylic acid do, releasing the CO2 gas that gives lime water its milky colour.
2: What are oxidising agents?
Answer: In a redox process, an oxidising agent is a reactant that steals electrons from other reactants. As an illustration, consider acidified potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7) and alkaline potassium permanganate (KMnO4).
Intext Exercise 5
1: Would you be able to check if water is hard by using a detergent?
Answer: The sodium or potassium salt of a lengthy chain of carboxylic acid is what makes soap. Ammonium or sulphonate salts of long-chain hydrocarbons are used as detergents. The sulphates and chloride of magnesium and calcium are found in hard water. A certain quantity of salt is wasted when soap is put to hard water since it produces less lather. Scum is the term for this insoluble salt. Both soft and hard water will produce a good amount of lather when using detergent. This does not allow us to determine the hardness or softness of water.
2: People use a variety of methods to wash clothes. Usually after adding the soap, they ‘beat’ the clothes on a stone, or beat it with a paddle, scrub with a brush or the mixture is agitated in a washing machine. Why is agitation necessary to get clean clothes?
Answer: Both components are found in soap. A portion of it is hydrophilic, whereas the other is hydrophobic. The sodium or potassium salt of a lengthy chain of carboxylic acid is what makes soap. when the soiled garments are submerged in the soapy liquid. The hydrophobic ends stick to the soil and group together in a massive way. The soil is held in place by this micelle-like cluster.
Best NCERT Solutions for Chapter 4 Science Class 10 Carbon And Its Compounds
NCERT Exercises
Question 1: How many covalent bonds are in C2H6?
(a) 6 covalent bonds.
(b) 8 covalent bonds.
(c) 7 covalent bonds.
(d) 5 covalent bonds.
Answer 1: (c) 7 covalent bonds.
2. What is the functional group in the Butanone?
(a) Ketone
(b) aldehyde.
(c) Ether
(d) alcohol.
Answer: (a) ketone.
3: When the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the outside while cooking, it shows that
(a) the food is cooked completely.
(b) the fuel is not burning completely.
(c) the food is not cooked.
(d) the fuel is burning completely.
Answer: (b) The bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the outside, then it means that the fuel is not burnt completely.
4: Explain the nature of the covalent bond using the bond formation in CH3Cl.
Answer: In nature, carbon is tetravalent. Four electrons make up carbon’s outermost shell. More energy is required to remove these electrons and to acquire the four electrons. Carbon must share its four electrons with other carbon atoms or with other atoms in order to complete the octet. With hydrogen, carbon creates three bonds, and with chlorine, it forms one.
5: Draw the cross dot structures of the following compounds.
(a) Ethanoic acid.
(b) H2S.
(c) Propanone.
(d) F2.
Answer:
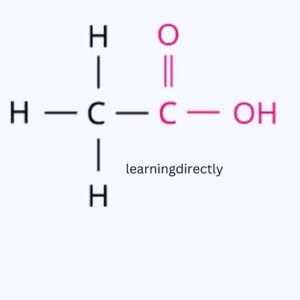
(a) Ethanoic acid.
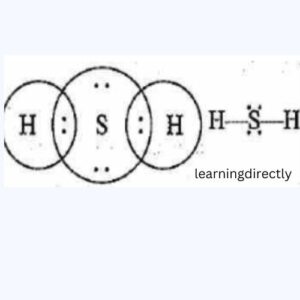
(b) H2S
(c) Propanone
(d) F2

6: What is a homologous series? Explain with an example.
Answer:
A homologous series is a group of carbon compounds that differ in their physical characteristics but share the same chemical properties. The homologous series is distinguished by the presence of -CH2.
The Alkanes family is one example. CnH2n+2 is the general formula for alkane.
CH4 methane
Ethane (CH3CH3)
Propane (CH3CH2CH3)
Butane (CH3CH2CH2CH3)
7: How can ethanol and ethanoic acid be differentiated on the basis of their physical and chemical properties?
Answer:
Physical properties: Ethanoic acid melts at 16.6 °C, while ethanol melts at -114.1 °C. Because of its low melting point, ethanolic acid freezes in the winter. At normal temperature, ethanol is a liquid, whereas ethanoic acid is solid. While ethanol smells good, ethanolic acid smells like vinegar.
Chemical Properties:
Ethanoic acid is a carboxylic acid, whereas ethanol is just alcohol. Alcohol and carboxylic acid together
A carboxylic acid combines with carbonates and bicarbonates to produce the CO2 gas that gives lime water its milky hue.
NaHCO3 or Na2CO3 plus CH3COOH H2O + CO2 + CH3COONa
8: In the electrolytic refining of a metal M, what would you take as the anode, the cathode and the electrolyte?
Answer:
When a metal M is refined electrolytically:
A pure metal anode
Cathode → Metal pure M
Salt solution of metal M in electrolyte
9: Why are carbon and its compounds used as fuels for most applications?
Answer:
Burning saturated carbon compounds with air produces carbon dioxide, light, and a lot of energy-rich water. There won’t be any smoke in this reaction, resulting in less pollution. The process is exothermic. Because of its high calorific value, it is utilised as fuel.
10: Explain the formation of scum when hard water is treated with soap.
Answer: The sodium or potassium salt of a lengthy chain of carboxylic acid is what makes soap. The sulphates and chloride of magnesium and calcium are found in hard water. A certain quantity of salt is wasted when soap is put to hard water since it produces less lather. Scum is the term for this insoluble salt.
11: What change will you observe if you test soap with litmus paper (red and blue)?
Answer: Because soap is fundamental in nature, blue litmus stays blue whereas red litmus turns blue.
12: What is hydrogenation? What is its industrial application?
Answer: Hydrogenation is the process of adding hydrogen to unsaturated molecules. The catalyst is Ni/Pt/Pd, and the reaction is addition-based. Compounds that are unsaturated change into saturated ones. The vegetable oil is transformed into ghee by this procedure.
13: Which of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition reactions:
C2H6, C3H8, C3H6, C2H2 and CH4.
Answer: There are addition reactions involving unsaturated hydrocarbons. The general formula for unsaturated hydrocarbons is CnH2n-2, or CnH2n. While C2H6, C2H8, and CH4 are saturated hydrocarbons in the provided compounds, C3H6 and C2H2 go through addition processes.
14: Give a test that can be used to differentiate chemically between butter and cooking oil.
Answer: Butter is saturated fat, but cooking oil is unsaturated fat. Butter does not react by hydrogenation, whereas oil does.
15: Explain the mechanism of the cleaning action of soaps.
Answer: Cleansing action of soaps:
Two components make up soap. A portion of it is hydrophilic, whereas the other is hydrophobic. The sodium or potassium salt of a lengthy chain of carboxylic acid is what makes soap. when the soiled garments are submerged in the soapy liquid. The hydrophobic ends stick to the soil and group together. The soil is held in place by this micelle-like cluster.