NCERT Solution For Class 9 Science Chapter 6 – Tissues
Exercise 6.1
- What is a tissue?
Solution:
A collection of cells with a similar structure that cooperate to carry out a certain function is referred to as a tissue.
NCERT Solution For Class 9 Science Chapter 6
- What is the utility of tissues in multicellular organisms?
Solution:
In multicellular organisms, tissues serve to allow for the division of labor as well as to give structural and mechanical strength.
Exercise 6.2 Page: 73
NCERT Solution For Class 9 Science Chapter 6
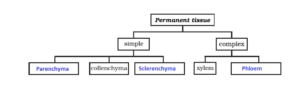
- Name the types of simple tissues.
Solution:
The types of simple tissues are as follows:
- ➢ Parenchyma
- ➢ Collenchyma
- ➢ Sclerenchyma
- Where is apical meristem found?
Solution:
In plants, the apical meristem is normally located at:
- The base of the plant
5. Which tissue makes up the husk of a coconut?
Solution:
The coconut husk is composed of a permanent tissue called sclerenchymatous tissue. The plant gets rigid and stiff from these tissues. Because of the lignin present, the tissue’s cells are dead and have thicker cell walls.
NCERT Solution For Class 9 Science Chapter 6
- What are the constituents of phloem?
Solution:
The phloem constitutes of the following four elements, they are:
➢ Sieve tube
➢ Companion cells
➢ Phloem parenchyma
➢ Phloem fibres
NCERT Solution For Class 9 Science Chapter 6
Exercise 6.3 Page: 77
- Name the tissue responsible for movement of our body.
Solution:
Two tissues jointly are responsible for the movement of our body, namely:
➢ Muscular tissue
➢ Nervous tissue
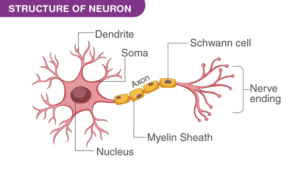
- What does a neuron look like?
Solution:
A nerve cell that has a cell body with a nucleus and cytoplasm from which a long, thin structure that resembles hair emerges is called a neuron. Each neuron consists of multiple short, thin branches called dendrites and one long segment called an axon. One neuron may even have a length of one meter.
NCERT Solution For Class 9 Science Chapter 6
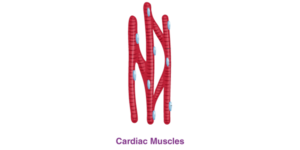
- Give three features of cardiac muscles.
Solution:
Cardiac muscles are specialized tissues that are evolved to pump blood throughout the body.
The following are the features of cardiac muscles:
➢ They are cylindrical in shape.
➢ Striated muscle fibers.
➢ They are uninucleated and branched.
➢ These muscles are involuntary in nature.
NCERT Solution For Class 9 Science Chapter 6
- What are the functions of areolar tissue?
Solution:
Animals are usually used to observe areolar tissues. They are the connective tissues that exist between the muscles and the skin. They exist in the bone marrow and are found near blood arteries and nerves. These tissues occupy the area inside the organs. They help restore damaged tissue and maintain the vulnerable interior organs.
Exercise Page: 78
- Define the term ’tissue’.
Solution:
A collection of cells with a similar structure that cooperate to carry out a certain function is referred to as a tissue.
- How many types of elements together make up the xylem tissue? Name them.
Solution:
The xylem tissue is made up of four main elements, namely:
➢ Vessels
➢ Tracheids
➢ Xylem fibres
➢ Xylem parenchyma
NCERT Solution For Class 9 Science Chapter 6
- How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants?
Solution:
The following are the differences:
| Simple tissues | Complex tissues |
| They are made up of a single type of cell that performs only one common function | They are made up of more than one kind of a cell that coordinate to perform one particular function |
- Differentiate between parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma on the basis of their cell wall.
Solution:
The following are the differences between different tissues based on cell wall:
| Parenchyma | Collenchyma | Sclerenchyma |
| Cell walls are thin and made up of cellulose | Cell walls are thick at the edges due to the deposition of pectin | Cell walls are thick due to the deposition of lignin |
NCERT Solution For Class 9 Science Chapter 6
- What are the functions of the stomata?
Solution:
Stomata are the microscopic pores found on the epidermis, the outermost layer of cells. Gas exchange and transpiration are facilitated by stomata.
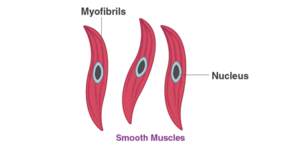
- Show the difference between the three types of muscle fibres diagrammatically.
Solution:
There are three types of muscle fibres, they are:
- Cardiac muscles
- Present in the heart.
- Involuntary in nature.
- They have 1 nucleus.
- The muscle fibers are branched.
- Smooth muscles
- Found in lungs and alimentary canal.
- Involuntary in nature.
- They have 1 nucleus.
- They are spindle-shaped.
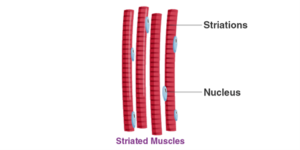
- Striated muscles
- They are connected with bones
- Voluntary in nature.
- They are long and cylindrical muscle fibers.
- They possess many nuclei.
- Striated muscles are unbranched.
NCERT Solution For Class 9 Science Chapter 6
- What is the specific function of the cardiac muscle?
Solution:
Circular and branching are the heart muscles. They possess an involuntary and uninitiated quality. Over an individual’s lifespan, the heart muscles produce a regular contraction and relaxation.
- Differentiate between striated, un-striated and cardiac muscles on the basis of their structure and site/location in the body.
Solution:
The following are the differences between different types of muscles, based on their structure and location in the body.
| Character | Striated muscles | Un-striated muscles | Cardiac muscles |
| Shape/Structure | Long, cylindrical, non – tapering.
They are un-branched. |
Long and tapering.
They are un-branched. |
Cylindrical and non – tapering.
They are branched. |
| Location in body | Hands, legs and skeletal muscles | Wall of stomach, intestine, ureter and bronchi | Heart |
| Dark and light bands | Present | Absent | Present but less prominent |
NCERT Solution For Class 9 Science Chapter 6
- Draw a labelled diagram of a neuron.
Solution:
Diagram of a neuron along with the labelling is as follows:

- Name the following.
(a) Tissue that forms the inner lining of our mouth.
(b) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans.
(c) Tissue that transports food in plants.
(d) Tissue that stores fat in our body.
(e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix.
(f) Tissue present in the brain.
Solution:
(a) Tissue that forms the inner lining of our mouth – The epithelial tissue, Squamous epithelium.
(b) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans – Tendon
(c) Tissue that transports food in plants – Phloem
(d) Tissue that stores fat in our body – Adipose tissue
(e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix – Blood, it is a fluid connective tissue
(f) Tissue present in the brain – Nervous tissue
NCERT Solution For Class 9 Science Chapter 6
- Identify the type of tissue in the following:
Skin, bark of tree, bone, lining of kidney tubule, vascular bundle.
Solution:
➢ Skin: Stratified squamous epithelial tissue
➢ Bark of tree: Protective tissue and cork
➢ Bone: Connective tissue
➢ Lining of kidney tubule: Cuboidal epithelial tissue
➢ Vascular bundle: Conducting tissue (xylem and phloem), complex permanent tissue
- Name the regions in which parenchyma tissue is present.
Solution:
The parenchyma is found in:
- The pith of stems and roots
- When parenchyma contains chlorophyll it is called a chlorenchyma. It is found in green leaves
- Parenchyma found in aquatic plants has large air cavities which enables them to float, and are hence called aerenchyma.
NCERT Solution For Class 9 Science Chapter 6
- What is the role of epidermis in plants?
Solution:
In plants, the epidermis forms a single, continuous layer without any gaps between cells. It offers security.
- How does the cork act as a protective tissue?
Solution:
Dead are the cork cells. There is no intercellular gap since the cell arrangement is so thick. It is noticed that suberin is deposited on the cell walls, rendering them impermeable to gasses and water.
- Complete the following chart.
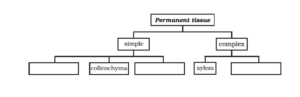
Solution:
The completed chart is as follows: