NCERT Solution For Class 9 Geography Chapter 3
Drainage

- Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below.
NCERT Solution For Class 9 Geography Chapter 3
i). Which one of the following describes the drainage patterns resembling the branches of a tree?
- Radial
- Dendritic
- Centrifugal
- Trellis
Ans. (b) Dendritic
ii). In which of the following states is the Wular lake located?
- Rajasthan
- Uttar Pradesh
- Punjab
- Jammu and Kashmir
Ans. (d) Jammu and Kashmir
iii). The river Narmada has its source at
- Satpura
- Brahmagiri
- Amarkantak
- Slopes of the Western Ghats
Ans. (c) Amarkantak
iv). Which one of the following lakes is a salt water lake?
- Sambhar
- Dal
- Wular
- Gobind Sagar
Ans. (a) Sambhar
v). Which one of the following is the longest river of the Peninsular India?
- Narmada
- Krishna
- Godavari
- Mahanadi
Ans. (c) Godavari
vi). Which one amongst the following rivers flows through a rift valley?
- Mahanadi
- Tungabhadra
- Krishna
- Tapi
Ans. (d) Tapi
NCERT Solution For Class 9 Geography Chapter 3
- Answer the following questions briefly.
i). What is meant by a water divide? Give an example.
Ans. A water divide is a range of mountains or a hill that divides two drainage basins. The Western Ghats, for instance.
ii). Which is the largest river basin in India?
Ans. India’s largest river basin is the Ganga river basin.
iii). Where do the rivers Indus and Ganga have their origin?
Ans. The Indus River originates in Tibet, close to the Mansarovar Lake, whereas the Ganga River originates in Uttarakhand state, at the Gangotri Glacier.
iv). Name the two headstreams of the Ganga. Where do they meet to form the Ganga?
Ans. The Ganga has two headstreams: Bhagirathi and Alaknanda. The Ganga is formed at Devprayag when they both meet.
v). Why does the Brahmaputra in its Tibetan part have less silt, despite a longer course?
Ans. There is not much silt carried by the Brahmaputra river, also called Tsangpo in Tibet, because it receives very little water there. However, it is nourished by copious amounts of rainwater once it leaves Arunachal Pradesh and enters India, carrying copious amounts of silt and water.
vi). Which two Peninsular rivers flow through trough?
Ans. In India, the Narmada and Tapi rivers flow through troughs. In contrast to deltas, they form estuaries as they enter the sea.
vii). State some economic benefits of rivers and lakes.
Ans. Rivers are excellent for hydroelectric power generation and agriculture. Inland waterways and fisheries are also provided by them. People can consume salt from lakes like Sambhar Lake. They also support the growth of tourism and offer leisure activities to individuals like Panging Tso.
- Below are given names of a few lakes of India. Group them under two categories – Natural and created by human beings.
- Wular
- Dal
- Nainital
- Bhimtal
- Gobind Sagar
- Loktak
- Barapani
- Chilika
- Sambhar
- Rana Pratap Sagar
- Nizam Sagar
- Pulicat
- Nagarjuna Sagar
- Hirakud
Ans. The Natural Lakes are: Wular, Dal, Nainital, Bhimtal, Chilika, Pulicat, Sambhar, Barapani, Loktak.
The Lakes created by human beings are: Gobind Sagar, Hirakud, Rana Pratap Sagar, Nagarjuna Sagar, Nizam Sagar.
NCERT Solution For Class 9 Geography Chapter 3
- Discuss the significant difference between the Himalayan and the Peninsular rivers.
Ans. The following is the comparison of the two rivers:
| S. No. | Himalayan Rivers | Peninsular Rivers |
| 1 | Himalayan rivers are perennial. | Peninsular rivers are seasonal. |
| 2 | They are fed by glaciers. | They receive water from the rainfall. |
| 3 | The Himalayan rivers are long and deep. | The peninsular rivers are short and shallow. |
| 4 | They carry a lot silt and sand. | They carry very no silt. |
| 5 | These rivers originate in the Himalayas in northern India. | These rivers originate in the Western Ghats. |
| 6 | Their drainage basins are large. | Their drainage basins are small. |
| 7 | These rivers form very large deltas. | They form very small or no deltas. |
NCERT Solution For Class 9 Geography Chapter 3
- Compare the east flowing and the west flowing rivers of the Peninsular plateau.
Ans. The following is the comparison of the two rivers:
| S. No. | East Flowing Rivers | West Flowing Rivers |
| 1. | They fall into the Bay of Bengal. | They fall into the Arabian Sea. |
| 2. | They form Estuaries | They form Deltas. |
| 3. | They have a large tributary network. | They have no tributary networks. |
| 4. | They do not flow through troughs. | They flow through troughs. |
NCERT Solution For Class 9 Geography Chapter 3
- Why are rivers important for the country’s economy?
Ans. Any nation’s economy depends on its rivers for a number of reasons, including:
- They serve as vital trade routes within the nation;
- They are a natural source of fresh water, which is necessary for all life to exist.• They are vital for commercial activity and are utilised for transportation and navigation
. • They also provide potential energy through the use of hydro power.Additionally, it offers fantastic recreational and scenic qualities for tourists. They are therefore excellent tourist destinations in the state.
(i) On an outline map of India mark and label the following rivers: Ganga, Satluj, Damodar, Krishna, Narmada, Tapi, Mahanadi, and Brahmaputra.
(ii) On an outline map of India mark and label the following lakes: Chilika Sambhar, Wular, Pulicat, Kolleru.
Ans:
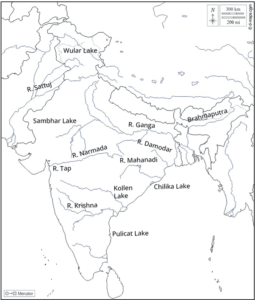
Outline Map of India mark Lakes

