NCERT Solution For Class 9 Geography Chapter 2
Physical Features Of India

1.A landmass bounded by sea on three sides is referred to as
a)Coast
b)Island
c)Peninsula
d)None of the above
Ans. (c) Peninsula
NCERT Solution For Class 9 Geography Chapter 2
2.Mountain ranges in the eastern part of India forming its boundary with Myanmar are collectively called as
a)Himachal
b)Uttarakhand
c)Purvanchal
d)none of the above
Ans. (c) Purvanchal
NCERT Solution For Class 9 Geography Chapter 2
3. The western coastal strip, south of Goa is referred to as
a)Coromandel
b)Konkan
c)Kannad
d)Northern Circars
Ans. (b) Kannad
NCERT Solution For Class 9 Geography Chapter 2
4.The highest peak in the Eastern Ghats is
a)Anai Mudi
b)Kanchenjunga
c)Mahendragiri
d)Khasi
Ans: (c) Mahendragiri
NCERT Solution For Class 9 Geography Chapter 2
5. Answer the following questions briefly.
- What are tectonic plates?
Ans: Tectonic plates are the large crustal fragments that are split apart by vertical currents.
- Which continents of today were part of the Gondwana land?
Ans: The landmass known as Gondwana included Antarctica, Peninsular India, South America, Australia, Africa (including Madagascar and its central and southern regions), and the Arabian Peninsula.
- What is bhabar?
Ans: The Bhabar region spans the banks of the upper Himalayan rivers, from the Indus to the Teesta, and is characterised by a narrow belt of pebbles rather than silt.
- Name the three major divisions of the Himalayas from north to south.
Ans: The Himalayas are divided into three main regions:
- The Great, Inner, or Himadri
- The Himachal Pradesh or Middle Himalayan region
- The Shivalik Mountains or the Outer Himalayas
6. Which plateau lies between the Aravali and the Vindhyan ranges?
Ans. The Vindhyan Range and the Aravali Range sandwich the Malwa plateau.
NCERT Solution For Class 9 Geography Chapter 2
7. Name the island group of India having coral origin.
Ans. The Indian group of islands known as the Lakshadweep Islands originated from coral.
8. Distinguish between:
- Converging and diverging tectonic plates
Ans: The difference between convergent and divergent tectonic plates are:
| Converging Tectonic Plates | Diverging Tectonic Plates |
| They move towards each other. | They move away from each other |
| They form fold mountains | They form rift valleys. |
NCERT Solution For Class 9 Geography Chapter 2
- Bhangar and Khadar
Ans: The difference between Bhangar and Khadar soils are:
| Bhangar | Khadar |
| It is old alluvial soil. | It is the new alluvium. |
| It is found in northern plains. | It is found in flood plains. |
| It has a terrace-like feature and is less fertile. | It is more fertile than the Bhangar. |
NCERT Solution For Class 9 Geography Chapter 2
- Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats
Ans. The difference between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats are:
| The Western Ghats | The Eastern Ghats |
| These ghats are found on the western side of the Deccan Plateau. | They lie on the eastern side of the Deccan Plateau. |
| They are higher and their average elevation is from 900 metres to 1600 meters. | They are lower as compared to the Western Ghats and their average elevation is about 600 meters. |
| They are a continuous chain of mountains and can be crossed only through passes. | These mountain ranges are not continuous and are broken by the rivers which flow into Bay of Bengal from the Western Ghats. |
| Major Rivers originate from these ranges. | Major rivers like Godavari, Krishna and Kaveri flow through them. |
9. Describe how the Himalayas were formed.
Ans: When the Earth first formed, Pangea was the only landmass, and the Tethys Sea, a vast body of water, was located where the Himalayas are today. The land was split into multiple sections as a result of plate tectonics beneath the Earth’s crust colliding and then rearranging. With slow movement to the north, the Indian and Eurasian plates collided to form the Himalayas, a system of fold mountains. These mountains are the youngest in the world’s formation. The Himalayas are still rising in height as a result of the plates’ continuous movement.
NCERT Solution For Class 9 Geography Chapter 2
10.Which are the major physiographic divisions of India? Contrast the relief of the Himalayan region with that of the Peninsular plateau.
Ans: The Himalayan Mountains and the Northern Plains are India’s two main physiographic divisions.
I. The islands;
- the Coastal Plains;
III. the Indian Desert;
- the Peninsular Plateau
11. Give an account of the Northern Plains of India.
Ans: Fertile alluvium from rivers that originated in the Himalayas has been deposited, creating the Northern Plains. They extend eastward from the Indian desert to the north of the peninsular plateau and south of the northern mountains. It is split into three sections: the Brahmaputra Plains, the Ganga Plains, and the Punjab Plains. The Northern Plains are roughly 3000 kilometres in length, and numerous rivers, including the Sutlej, Ravi, Beas, Ganga, Yamuna, Ghagra, Gandak, Kosi, Chambal, Betwa, Son, and others, drain this area.
There are four zones that make up the North Indian Plains:
1. Bhabar
2. Tarai
3. Bagar
4. Khadar
YOU CAN ALSO FOLLOW US ON SOCIAL MEDIA
12. Write short notes on the following.
- The Indian Desert
Ans: The Thar Desert, another name for the Great Indian Desert, is found in Pakistan’s Punjab and Sindh as well as India’s Rajasthan state. There is also desert land in the states of Gujarat and Haryana.
There are very few water sources in the extremely dry Thar desert, which lies between Pakistan and India. The only places to find water are the ponds that have been created by humans and by nature. As a result, the majority of the population leads a nomadic lifestyle, moving frequently throughout their life. In the Thar desert, the Luni River is a significant river that drains a sizable portion of the region. In the northern and eastern regions of the desert flows Ghaggar, the other significant river.
NCERT Solution For Class 9 Geography Chapter 2
- The Central Highlands
Ans: The Central Highlands constitute a significant portion of the Malwa plateau and are located to the north of the Narmada River on the peninsular plateau. The rivers that drain this area flow because of their slope from southwest to northeast. The Central Highlands taper off towards the east from their wider western portion. Bundelkhand and Baghelkhad are the names given to them in Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, and Chhattisgarh. Situated to the east of the Central Highlands, the Chotanagpur plateau is traversed by the Damodar River.
- The Island groups of India
Ans: India is in charge of two island groups. They are situated in the Bay of Bengal (Andaman and Nicobar Islands) and the Arabian Sea (Lakshadweep Islands). These islands are off the Indian coast of Malabar. The Lakshadweep Islands, with Kavaratti as their capital, are the second-smallest Union territory in terms of population and area. India benefits from having the Islands of Lakshadweep as a strategic base in the Arabian Sea, and at key moments, it can communicate with the Maldives and other parts of the Indian Ocean.
The 572 islands that make up the Andaman and Nicobar Islands group. India can easily reach Southeast Asian countries thanks to the Nicobar Islands’ proximity to the Sumatra Islands. The Indian Navy also keeps a base in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, which aids in its ability to control ships that pass through the Strait of Malacca. The most primitive members of humanity, known as the Sentinelese people, live on the North Sentinel Island in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. They are unaffected by civilization.
NCERT Solution For Class 9 Geography Chapter 2
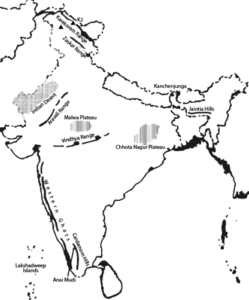
Map Skills:
On an outline map of India show the following.
- Mountain and hill ranges – the Karakoram, the Zaskar, the Patkai Bum, the Jaintia, the Vindhya range, the Aravali, and the Cardamom hills.
- Peaks – K2, Kanchenjunga, Nanga Parbat and the Anai Mudi.
iii. Plateaus, Chotanagpur and Malwa
- The Indian Desert, Western Ghats, Lakshadweep Islands
Ans: